[백준 1520번 C/C++] 내리막 길
[백준 1520번 C/C++] 내리막 길

https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1520
1520번: 내리막 길
여행을 떠난 세준이는 지도를 하나 구하였다. 이 지도는 아래 그림과 같이 직사각형 모양이며 여러 칸으로 나뉘어져 있다. 한 칸은 한 지점을 나타내는데 각 칸에는 그 지점의 높이가 쓰여 있으
www.acmicpc.net
해결전략
깊이우선탐색 + 다이나믹 프로그래밍, Dynamic Programming
DFS + DP (= 메모이제이션)
DFS로만 풀면 시간초과가 나온다.
DFS 풀이: 시간초과
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; int dirY[4] = { -1, 0, 1, 0 }; int dirX[4] = { 0, -1, 0, 1 }; int r, c; // 행, 열 int answer; // 경로의 개수 vector<vector<int>> v; vector<vector<int>> ch; void DFS(int y, int x){ if (y == r - 1 && x == c - 1) { answer++; return; } for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int ny = y + dirY[i]; int nx = x + dirX[i]; if (ny < 0 || r <= ny || nx < 0 || c <= nx) continue; if (ch[ny][nx] == 0 && v[ny][nx] < v[y][x]) { ch[ny][nx] = 1; DFS(ny, nx); ch[ny][nx] = 0; } } } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); cin >> r >> c; v.resize(r, vector<int>(c)); ch.resize(r, vector<int>(c)); for (int y = 0; y < r; y++) { for (int x = 0; x < c; x++) { cin >> v[y][x]; } } DFS(0, 0); cout << answer; return 0; }
정답코드: DFS + DP (= 메모이제이션)
도착 지점으로부터 거꾸로 시작 지점으로 경로를 추적하면서 경로의 수를 계산한다!
ch[ y ][ x ]의 값은 해당 위치(y, x)에서 목적지(r-1, c-1)까지의 경로의 수다.
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; int dirY[4] = { -1, 0, 1, 0 }; int dirX[4] = { 0, -1, 0, 1 }; int r, c; // r: 행, c: 열 long long answer; // 경로 개수 vector<vector<int>> v; vector<vector<int>> ch; // 방문 처리 & 경로 개수 캐싱. -1은 미방문 상태. ch배열 원소들의 값은 해당 위치(y, x)에서 목적지(r-1, c-1)까지 경로 개수. void DFS(int y, int x){ if (y == r - 1 && x == c - 1) return; // 도착 지점에 도달했을 경우 if (ch[y][x] != -1) return; // 이미 방문한 경우(=경로개수 이미 계산됨). ch[y][x] = 0; // (y, x) 방문표시. 아래에서 경로개수 계산. for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int ny = y + dirY[i]; int nx = x + dirX[i]; if (ny < 0 || r <= ny || nx < 0 || c <= nx) continue; if (v[y][x] <= v[ny][nx]) continue; if (ch[ny][nx] == -1){ // 아직 방문한적이 없다면 DFS 탐색. //cout << ny << ", " << nx << "\n"; DFS(ny, nx); ch[y][x] += ch[ny][nx]; // 탐색 후 현재 위치의 경로개수 업데이트 //cout << "Calculation: " << ny << ", " << nx << "\n"; } else { // 방문한적이 있는 경우 ch[y][x] += ch[ny][nx]; // 이미 계산된 경로 수를 현재 위치에 추가 } } } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); cin >> r >> c; v.resize(r, vector<int>(c)); ch.resize(r, vector<int>(c, -1)); // -1을 초기값으로 설정. -1은 미방문 상태. for (int y = 0; y < r; y++) { for (int x = 0; x < c; x++) { cin >> v[y][x]; } } // 이 코드에서 도착점은 경로 계산의 기준점이다. 도착 지점에서 시작하여 거꾸로 이동하면서 경로의 수를 계산한다. // 도착 지점의 경로 수를 1로 설정함으로써, 모든 경로 계산의 출발점이 된다. ch[r-1][c-1] = 1; DFS(0, 0); // 시작 지점에서 DFS 시작 cout << ch[0][0]; // 시작지점(0, 0)에서 도착지점(r-1, c-1)까지의 경로의 수 return 0; }
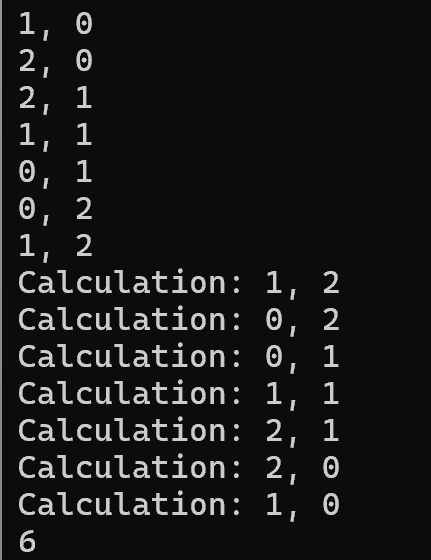
[ 반례 예시 ]
3 3
9 4 3
8 5 2
7 6 1
답: 6
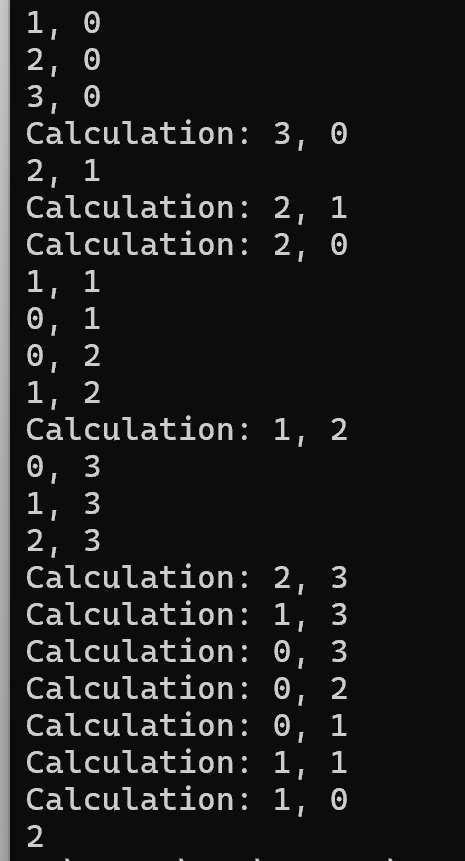
4 4
93 72 61 58
90 73 19 49
85 36 75 13
21 41 45 7
답: 2
'⭐ 코딩테스트 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준 16236번 C/C++] 아기 상어 (0) | 2024.05.04 |
|---|---|
| [백준 14499번 C/C++] 주사위 굴리기 (0) | 2024.05.04 |
| [백준 7682번 C/C++] 틱택토 (1) | 2024.04.20 |
| [백준 15864번 C/C++] 사다리 조작 (1) | 2024.04.19 |
| [백준 6087번 C/C++] 레이저 통신 (0) | 2024.04.16 |
댓글
이 글 공유하기
다른 글
-
[백준 16236번 C/C++] 아기 상어
[백준 16236번 C/C++] 아기 상어
2024.05.04 -
[백준 14499번 C/C++] 주사위 굴리기
[백준 14499번 C/C++] 주사위 굴리기
2024.05.04 -
[백준 7682번 C/C++] 틱택토
[백준 7682번 C/C++] 틱택토
2024.04.20 -
[백준 15864번 C/C++] 사다리 조작
[백준 15864번 C/C++] 사다리 조작
2024.04.19
댓글을 사용할 수 없습니다.