[C++] 상속성
상속성
인프런 Rookiss님의 'Part1: C++ 프로그래밍 입문' 강의를 기반으로 정리한 필기입니다.
😎[C++과 언리얼로 만드는 MMORPG 게임 개발 시리즈] Part1: C++ 프로그래밍 입문 강의 들으러 가기!
상속성
- 클래스로부터 멤버들을 물려받는 것.
- 자식 클래스는 부모 클래스의 멤버 변수와 멤버 함수를 사용할 수 있다.
- 자식 클래스는 자신만의 변수와 멤버 함수를 추가할 수 있다.
- 또한 부모 클래스에 존재하는 멤버 함수를 재정의 할 수 있다.
- 상속은 is-a 관계이다 = "~은 ~이다" 관계가 성립되는지 확인
부모 클래스로부터 상속받은 특징들을 자식 클래스에서 추가, 교체, 구체화시킬 수 있다.
객체지향 3요소(OOP Object Oriented Programming)
- 상속성
- 은닉성
- 다형성
상속(Inheritance) + 생성자, 소멸자
상속(Inheritance)
- 부모 -> 자식에게 유산을 물려주는 것
메모리
- 부모의 메모리 크기 만큼 먼저 만든 다음, 자식의 데이터가 더 많으면 메모리를 추가한다.
[ [ Player ] ]
[ Knight ]
생성자와 소멸자
- 생성자 (N개 가능) / 소멸자(1개)
- 생성자는 탄생을 기념해서 호출되는 함수?
- Knight를 생성하면 -> Player의 생성자? Knight의 생성자? 둘 중 뭐를 호출해야 할까?
- 솔로몬의 선택! 그냥 둘 다 호출하자!
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct StatInfo{
int _hp;
int _attack;
int _defence;
};
class Player
{
public:
Player()
{
_hp = 0;
_attack = 0;
_defence = 0;
cout << "Player() 기본 생성자 호출" << endl;
}
~Player()
{
cout << "~Player() 소멸자 호출" << endl;
}
void Move() { cout << "Player Move 호출" << endl; }
void Attack() { cout << "Player Attack 호출" << endl; }
void Die() { cout << "Player Die 호출" << endl; }
public:
int _hp;
int _attack;
int _defence;
};
class Knight : public Player // class는 일종의 설계도
{
public:
Knight()
//** 선(먼저)처리 영역
//** - 여기서 Player() 생성자를 호출
{
_stamina = 100;
cout << "Knight() 기본 생성자 호출" << endl;
}
~Knight()
{
cout << "~Knight() 소멸자 호출" << endl;
}
//** 후(나중에)처리 영역
//** - 여기서 ~Player() 소멸자를 호출
// 재정의 : 부모님의 유산을 거부하고 새로운 이름으로 만듬
void Move() { cout << "Knight Move 호출" << endl; }
public:
int _stamina;
};
class Mage : public Player{
public:
int _mp;
};
int main()
{
Knight k;
return 0;
}
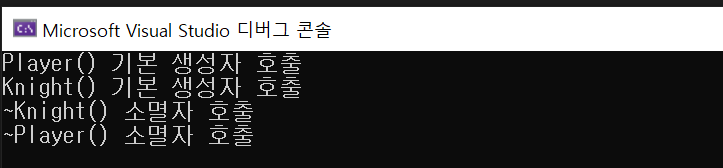
생성 순서: 부모 클래스가 먼저 생성되고 그 다음에 자식 클래스가 생성된다.
소멸 순선: 소멸되는 순서는 자식이 먼저 소멸, 그 다음 부모님이다.
순서를 꼭 기억하자.
예시 코드들
예시 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct StatInfo{
int _hp;
int _attack;
int _defence;
};
class Player{
public:
Player()
{
_hp = 0;
_attack = 0;
_defence = 0;
cout << "Player() 기본 생성자 호출" << endl;
}
Player(int hp)
{
_hp = hp;
_attack = 0;
_defence = 0;
cout << "Player(int hp) 생성자 호출" << endl;
}
~Player()
{
cout << "~Player() 소멸자 호출" << endl;
}
void Move() { cout << "Player Move 호출" << endl; }
void Attack() { cout << "Player Attack 호출" << endl; }
void Die() { cout << "Player Die 호출" << endl; }
public:
int _hp;
int _attack;
int _defence;
};
class Knight : public Player
{
public:
Knight()
/*
선(먼저)처리 영역
- 여기서 Player() 생성자를 호출
*/
{
_stamina = 100;
cout << "Knight() 기본 생성자 호출" << endl;
}
Knight(int stamina) : Player(100)
/*
선(먼저)처리 영역
- 여기서 Player(int hp) 생성자를 호출
*/
{
_stamina = stamina;
cout << "Knight(int stamina) 생성자 호출" << endl;
}
~Knight()
{
cout << "~Knight() 소멸자 호출" << endl;
}
/*
후(나중에)처리 영역
- 여기서 ~Player() 소멸자를 호출
*/
// 재정의 : 부모님의 유산을 거부하고 새로운 이름으로 만듬
void Move() { cout << "Knight Move 호출" << endl; }
public:
int _stamina;
};
class Mage : public Player
{
public:
int _mp;
};
int main()
{
Knight k(100);
return 0;
}실행화면

예시2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct StatInfo{
int _hp;
int _attack;
int _defence;
};
class Player{
public:
Player()
{
_hp = 0;
_attack = 0;
_defence = 0;
cout << "Player() 기본 생성자 호출" << endl;
}
Player(int hp)
{
_hp = hp;
_attack = 0;
_defence = 0;
cout << "Player(int hp) 생성자 호출" << endl;
}
~Player()
{
cout << "~Player() 소멸자 호출" << endl;
}
void Move() { cout << "Player Move 호출" << endl; }
void Attack() { cout << "Player Attack 호출" << endl; }
void Die() { cout << "Player Die 호출" << endl; }
public:
int _hp;
int _attack;
int _defence;
};
class Knight : public Player
{
public:
Knight()
/*
선(먼저)처리 영역
- 여기서 Player() 생성자를 호출
*/
{
_stamina = 100;
cout << "Knight() 기본 생성자 호출" << endl;
}
Knight(int stamina) : Player(100)
/*
선(먼저)처리 영역
- 여기서 Player(int hp) 생성자를 호출
*/
{
_stamina = stamina;
cout << "Knight(int stamina) 생성자 호출" << endl;
}
~Knight()
{
cout << "~Knight() 소멸자 호출" << endl;
}
/*
후(나중에)처리 영역
- 여기서 ~Player() 소멸자를 호출
*/
// 재정의 : 부모님의 유산을 거부하고 새로운 이름으로 만듬
void Move() { cout << "Knight Move 호출" << endl; }
public:
int _stamina;
};
class Mage : public Player
{
public:
int _mp;
};
int main()
{
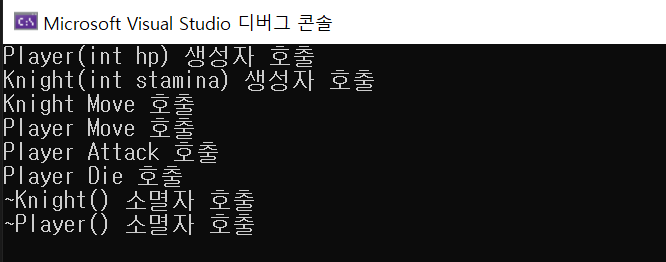
Knight k(100);
k._hp = 100;
k._attack = 10;
k._defence = 5;
k._stamina = 50;
k.Move(); // 자식이 재정의한 Move 호출
k.Player::Move(); // 부모님의 Move 호출.
// 재정의해서 다음과 같이 쓰는 경우는 매우 드물다.
k.Attack();
k.Die();
return 0;
}
실행화면
'⭐ Programming > C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++] 다형성 (Polymorphism) (0) | 2022.04.05 |
|---|---|
| [C++] 은닉성 (0) | 2022.04.04 |
| [C++] 생성자와 소멸자 2 (0) | 2022.04.04 |
| [C++] 생성자와 소멸자 (0) | 2022.04.04 |
| [C++] 객체지향 (0) | 2022.04.03 |
댓글
이 글 공유하기
다른 글
-
[C++] 다형성 (Polymorphism)
[C++] 다형성 (Polymorphism)
2022.04.05 -
[C++] 은닉성
[C++] 은닉성
2022.04.04 -
[C++] 생성자와 소멸자 2
[C++] 생성자와 소멸자 2
2022.04.04 -
[C++] 생성자와 소멸자
[C++] 생성자와 소멸자
2022.04.04