[알고리즘] 우선순위 큐 Priority Queue
글의 요약 설명 부분. 150자를 적어주세요. 글의 요약 설명 부분. 150자를 적어주세요. 글의 요약 설명 부분. 150자를 적어주세요. 글의 요약 설명 부분. 150자를 적어주세요. 글의 요약 설명 부분. 150자를 적어주세요. 글의 요약 설명 부분. 150자입니다
목차
우선순위 큐 Priority Queue
본문내용
공통코드
|
template<typename T, typename Container = vector<T>, typename Predicate = less<T>>
class PriorityQueue
{
public:
void push(const T& data) {...}
void pop() {...}
T& top() { return _heap[0];
bool empty() { return _heap.empty(); }
private:
Container _heap = {};
Predicate _predicate = {};
};
int main()
{
PriorityQueue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq;
pq.push(100);
pq.push(300);
pq.push(200);
pq.push(500);
pq.push(400);
while (pq.empty() == false)
{
int value = pq.top();
pq.pop();
cout << value << endl;
}
}
|
cs |
힙의 삽입 연산
힙의 삽입 연산은 다음 아래의 과정을 거쳐 이루어진다.
- 최고 깊이 최우측에 [새 노드]를 추가한다. 단, 힙은 완전 이진 트리를 유지해야 한다.
- [새 노드]와 [부모 노드]를 비교한다.
- [새 노드] > [부모 노드] 경우 연산을 종료한다.
- [새 노드] < [부모 노드] 경우 다음 단계를 진행한다.
- [새 노드]와 [부모 노드]의 위치를 바꾸어준다. 위치를 바꾼 후 2단계를 다시 진행한다.

|
void push(const T& data)
{
// 우선 힙 구조부터 맞춰준다
_heap.push_back(data);
// 도장깨기 시작, 아래에서부터 부모 노드와 비교하며 진행한다
int now = static_cast<int>(_heap.size()) - 1;
// 루트 노드까지
while (now > 0)
{
// 부모 노드와 비교해서 더 작으면 패배
int next = (now - 1) / 2;
//if (_heap[now] < _heap[next])
// break;
if (_predicate(_heap[now], _heap[next]))
break;
// 데이터 교체
::swap(_heap[now], _heap[next]);
now = next;
}
}
|
cs |
힙의 최소값 삭제 연산
뿌리 노드 = 힙에서 가장 작은 데이터를 갖는 노드
따라서, 힙의 최소값 삭제는 뿌리 노드를 삭제한다는 말이다.
뿌리 노드 삭제 후 뒤처리 과정은 다음과 같다.
- 최고 깊이 최우측 노드를 뿌리 노드로 옮긴다.
- 옮겨온 노드를 양쪽 자식 노드와 비교하여 작은 쪽 자식과 위치를 교환한다.
- 자식이 없는 잎 노드가 되거나 양쪽 자식 노드보다 작은 값이 될 때까지 교환한다.
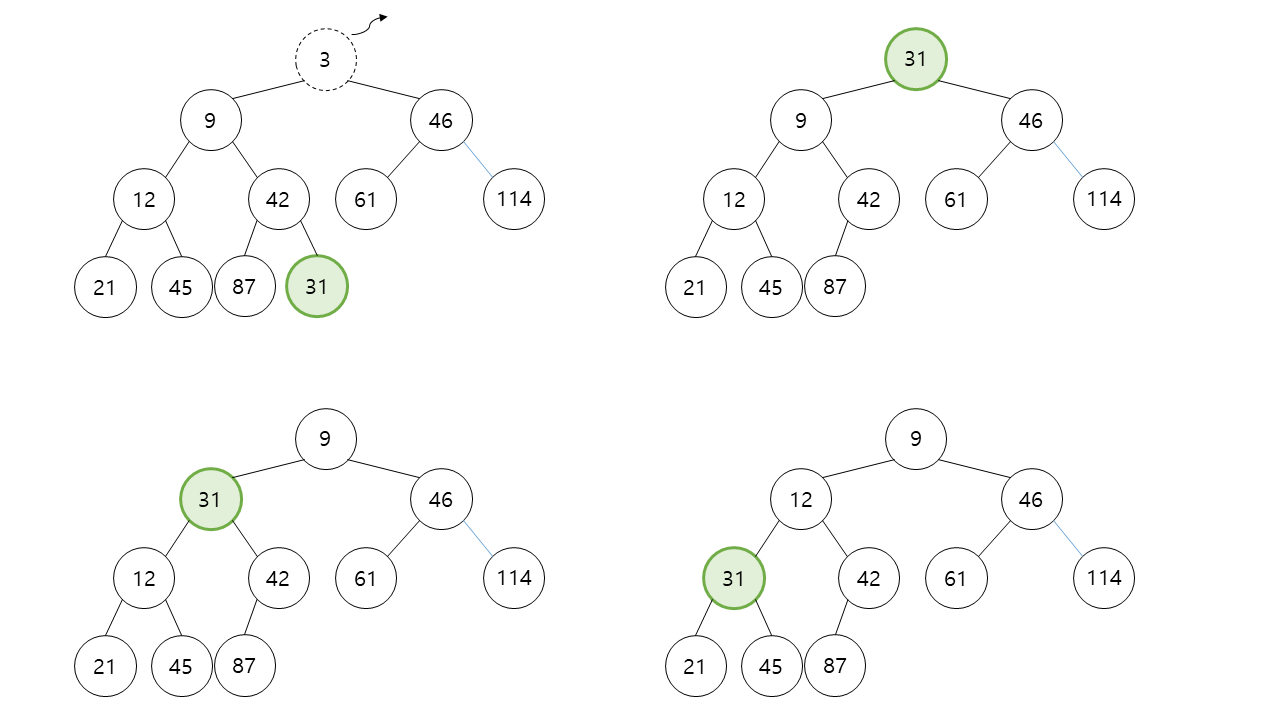

|
void pop()
{
_heap[0] = _heap.back();
_heap.pop_back();
int now = 0;
while (true)
{
int left = 2 * now + 1;
int right = 2 * now + 2;
// 리프에 도달한 경우
if (left >= (int)_heap.size())
break;
int next = now;
// 왼쪽과 비교
//if (_heap[next] < _heap[left])
// next = left;
if (_predicate(_heap[next], _heap[left]))
next = left;
// 둘 중 승자를 오른쪽과 비교
if (right < (int)_heap.size() && _predicate(_heap[next], _heap[right]))
next = right;
// 왼쪽/오른쪽 둘 다 현재 값보다 작으면 종료
if (next == now)
break;
::swap(_heap[now], _heap[next]);
now = next;
}
}
|
cs |
힙의 구현
힙은 완전 이진 트리이다. 완전 이진 트리는 배열로 구현할 수 있다.
배열을 이용해서 힙 구조를 바로 표현할 수 있다.
- i번 노드의 왼쪽 자식은 [ (2 * i) + 1 ]번
- i번 노드의 오른쪽 자식은 [ (2 * i) + 2 ]번
- i번 노드의 부모는 [ (i - 1) / 2 ]번

전체코드
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
template<typename T, typename Container = vector<T>, typename Predicate = less<T>>
class PriorityQueue
{
public:
void push(const T& data)
{
// 우선 힙 구조부터 맞춰준다
_heap.push_back(data);
// 도장깨기 시작, 아래에서부터 부모 노드와 비교하며 진행한다
int now = static_cast<int>(_heap.size()) - 1;
// 루트 노드까지
while (now > 0)
{
// 부모 노드와 비교해서 더 작으면 패배
int next = (now - 1) / 2;
//if (_heap[now] < _heap[next])
// break;
if (_predicate(_heap[now], _heap[next]))
break;
// 데이터 교체
::swap(_heap[now], _heap[next]);
now = next;
}
}
void pop()
{
_heap[0] = _heap.back();
_heap.pop_back();
int now = 0;
while (true)
{
int left = 2 * now + 1;
int right = 2 * now + 2;
// 리프에 도달한 경우
if (left >= (int)_heap.size())
break;
int next = now;
// 왼쪽과 비교
//if (_heap[next] < _heap[left])
// next = left;
if (_predicate(_heap[next], _heap[left]))
next = left;
// 둘 중 승자를 오른쪽과 비교
if (right < (int)_heap.size() && _predicate(_heap[next], _heap[right]))
next = right;
// 왼쪽/오른쪽 둘 다 현재 값보다 작으면 종료
if (next == now)
break;
::swap(_heap[now], _heap[next]);
now = next;
}
}
T& top()
{
return _heap[0];
}
bool empty()
{
return _heap.empty();
}
private:
Container _heap = {};
Predicate _predicate = {};
};
int main()
{
//PriorityQueue<int> pq;
PriorityQueue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq; //less로 변경 시 역순
pq.push(100);
pq.push(300);
pq.push(200);
pq.push(500);
pq.push(400);
while (pq.empty() == false)
{
int value = pq.top();
pq.pop();
cout << value << endl;
}
}
|
cs |

'⭐ Programming > 자료구조와 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘] Heap Sort, Merging Sort 힙 정렬, 병합 정렬 (0) | 2022.11.01 |
|---|---|
| [알고리즘] 정렬 Sorting (0) | 2022.11.01 |
| [자료구조] 이진 트리, 힙 이론, 힙 트리 (0) | 2022.10.31 |
| [자료구조] 트리 기초 (0) | 2022.10.31 |
| [자료구조] 다익스트라 알고리즘 (0) | 2022.10.31 |
댓글
이 글 공유하기
다른 글
-
[알고리즘] Heap Sort, Merging Sort 힙 정렬, 병합 정렬
[알고리즘] Heap Sort, Merging Sort 힙 정렬, 병합 정렬
2022.11.01 -
[알고리즘] 정렬 Sorting
[알고리즘] 정렬 Sorting
2022.11.01 -
[자료구조] 이진 트리, 힙 이론, 힙 트리
[자료구조] 이진 트리, 힙 이론, 힙 트리
2022.10.31 -
[자료구조] 트리 기초
[자료구조] 트리 기초
2022.10.31